
Komal TexFab Organisational management Case-study
Management research | Organisation study | Audit | Strategic Road-map
Scope of the Project
The scope of this project is to study KOMAL TEXFAB to its core and to conduct a design audit for that organisation. The design audit examines the internal and external functioning of the organisation to identify gaps and opportunities for reorienting or rebuilding the strategy and vision of the organisation.
Team
Kasturika | Prashansa | Ruchi | Garima
8 weeks
Timeline
Project type
Client work
Research approach
Research approach

Objectives
The approach to the audit has been multi-layered,
interconnected, and multi-faceted to be able to scan and assess in 360 degrees
-
DECODING COMPLEX V/S COMPLICATED
-
GOING BEYOND THE NUMBERS
-
HOLISTIC PERSPECTIVE
-
REACH TO THE ROOTS OF THE PROBLEMS
-
DIAGNOSE THE INTANGIBLES
Outcomes
Dealing with the audit like a management case study, outcomes will be
-
ASSESSING ORGANISATIONAL HEALTH
-
STRATEGIC ROAD MAP TO IMPROVE MANAGEMENT AND RELATED ISSUES
RESEARCH FLOW

Methodology
Understanding each department in-depth and getting an idea of the roles and responsibilities of employees and their expectations from the company. Level of penetration of information and values into each segment
and identifying hindrances and bottlenecks involved

Discover
Understanding departments their roles and co-ordination, management and leadership
ABOUT KOMAL TEXFAB
To be a leading textile solution provider enterprise across the domestic and global markets by exceeding customer expectations. To continuously explore the untapped potential markets & products.
SEZ Unit
Vision and Mission
Komal Texfab Pvt. ltd. expanded with launching their new vertical catering the apparel market in 2011. The objective of this unit was to look into the export & domestic markets dealing with the orders outsourced by these.
Organizational Structure
The structure of the organization here in SEZ looks like this, There are 45 Full-time staff members and about 300 workers working on contract basis.


SWOT & PESTEL Analysis




Verbatims from different departments and leaderships
Leadership and management concerns
Findings from witness and encounter



Hypothesis
Based on the findings so far, we created the hypothesis to further validate and understand the root cause of the issues through our research.


Validate
Validate
Validate
Validation of hypothesis and surfacing out data to analyse
PURCHASE ORDER TRACKING
1
To understand the core problem and specially within the existing communication system. To identify the issues in the small process of material procurement.
There is no accountability of the purchase order placed. Could not check the profit and loss the SEZ unit is making with each purchase made in order to track the growth of the organisation.

Artefact study
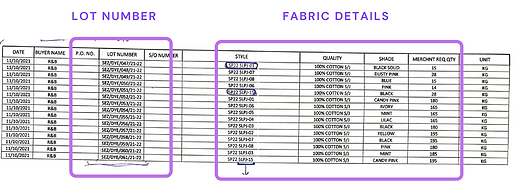
-
Lot Number is Issued to the MERCHANT.
-
Excel file is only maintained by Fabric procurement head.
-
The information is not shared with the store department head

-
Multiple nomenclature for the same number increases chances of error
-
The card is number based and there is no visual identification
-
A number of details are not required and are un-necessary for departments
-
MIF is shared with the Accountant to prepare Tally P.O.
-
Un-necessary information is shared by the Merchant Accountant and Mill leading to confusion and repetitive tasks being performed at every stage, increasing the chances of human errors.


Findings from PO tracking
2
DATA | PEOPLE | THING
94%
gave importance to 'Style number'and 'shade/colour'


Merchants send formal mails to vendors for orders,
however, they call the vendor to remind and confirm with
them about the mail that has been sent. Mails also act as a
proof for orders
@

SWATCHES & SAMPLES
Multiple channels to communicate the same message, that leads to wastage of time and un-necessary cognitive load
COGNITIVE LOAD
Employees mostly use swatches and samples to identify styles, orders and designs.
BACKUP OF BACKUPS
Multiple backup channels are created for every information that is to be shared like mails, whatsapp, physical files, excel sheets.
UNDOCUMENTED DOCUMENTS
Due to one-on-one discussions, calls and whatsapp most of the information is either not documented or updated much later.

3
CIRCULAR CONVERSATION

PLANNER
-
Constant follow up is required to get the tasks done.
-
Sometimes order quantity is not fulfilled by production dept. and they ship less than quoted.
-
Merchants are frustrated most of the times due to high pressure and missing the PP comments.
PRODUCTION TEAM
-
Decision making gets affected due to slow work of merchandising team. Mis-communication and merchants forget to tell important information and most of the time gets wasted in recollecting it.
-
Daily work report is shared with the CEO and merch. manager as per the tasks allotted by the planner.
-
Constant contradictions between Merchandising & Quality teams in terms of details, specifications and fast delivery.
MERCHANDISE TEAM
-
The production departments are not accountable for the work they are doing. They do not take deadlines seriously.
-
Planner is very responsible regarding his work, takes accountability for actions and goes out of his way to help.
-
Fabric cutting is done prior to approval. A lot of times files get mixed up and wrong patterns are cut out of the fabric resulting in loss.
-
Work gets delayed due to laziness of accounts dept. Thus they go out of their way to get the work done.
CAD TEAM
-
Sometimes the instructions in the file aren't sufficient so they have to be coordinated physically and face issues in meeting deadlines from merchants' end.
Analyze
Analysis of data collected to chalk-out the strategic roadmap
ATTRITION RATE
People currently working at Komal
72%
WOULD LEAVE AS SOON AS THEY
RECIEVE A BETTER OPPORTUNITY
18%
LIKELY OR ALMOST CERTAIN
TO LEAVE AT PRESENT
During COVID
25%
PEOPLE AT STAFF LEVEL
LEFT THE ORGANISATION
Why do people leave?
-
When employers were asked, why their people had quit, they cited compensation, personal work-lifechanges, better opportunities and growth.
-
These issues did matter to employees - but not as much as employers thought they did. Employees are far more likely to prioritize relational factors, whereas employers were more likely to focus on transactional ones.

Why do people leave?
-
A record number of employees are quitting or thinking about doing so. it's time for organizations to take time to learn 'why' and then act
-
thoughtfully. By doing so, the organisation will have an edge attracting and retaining talent.
EMPLOYERS DO NOT FULLY UNDERSTAND WHY EMPLOYEES ARE LEAVING


LEADERSHIP CHALLENGES
MANAGEMENT SHIFT
-
Highlighting the situation at Komal by mapping the Principles, processes, and practices of
-
20th-century v/s 21st-century management

WHY ANALYSIS
-
After doing 'Why analysis' we put the major issues on the radar map to get an overall idea of the core issues under 4 categories. Since most of the issues are interlinked and are there due to cascading effects of a few core issues

PROCESSES AND SYSTEM ISSSUE
INFORMATION STRUCTURE AND FLOW
MANAGEMENT
ISSUE
BEHAVIOURAL
ISSUE
ORGANIZATION'S HEALTH
How healthy is an organization?
-
Organizational health is more than culture and employee engagement; it is the organization's ability to align around a shared vision, execute against those visions effectively and renew itself through innovation and creative thinking source


After mapping the various attributes, we came across the key aspects seeking special attention in the organization.
The parameters with score of 2 or less are the affected zones of the company
Develop
Approaches and suggestions with the time-line

STRATEGIC ROAD MAP




